Introduction (RDS/CCI)
RDS (reference designation system) origins from the standard series of IEC/ISO 81346 and is used to define information structuring principles. IEC/ISO 81346 also provides classification system tables that can be used for various domains, including built environment. Several construction classification systems are based on the RDS classification system tables (e.g. CCI, CoClass).
CCI stands for Construction Classification International (CCI) and it is a classification system for the built environment developed by the CCIC (Construction Classification International Collaboration) consortium, which today is largely equivalent to the RDS classification system tables. The RDS/CCI core framework is based on the EN ISO 12006-2 standard and covers the part related to construction result (see figure below, green boxes – so-called core tables).
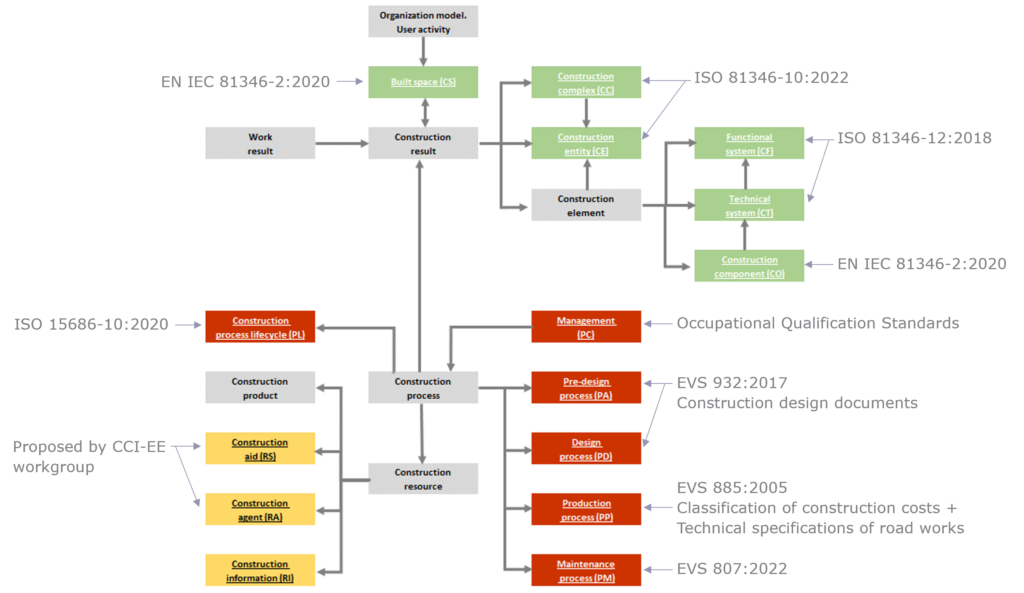
CCI-EE adds several additional tables to the RDS/CCI core tables, focusing on parts of the construction process and construction resource. These tables are based on international standards, but also partly on local (Estonian) standards. These integrated standards have been adjusted to fit with the construction result section with a clear purpose not to duplicate what is already presented in other tables. This creates an integrated, the whole life-cycle-based, construction classification system.
- RDS/CCI core tables can be accessed from: https://cci-collaboration.org
- CCI-EE tables (together with RDS/CCI tables and bilingually – Estonian/English) can be downloaded from the Estonian Construction Centre website: https://ehituskeskus.ee/cci/ee-tabelid/
In the following parts, we will see how mainly RDS/CCI core tables can be implemented through various software solutions (both building and infrastructure domains). It is important to emphasize that regardless of the software used, we should ensure a unified, structured reuse of information in any application (or format) which would be both human- and machine readable.